前言
大家都知道python是个万能胶水语言,有很多库,可以解决很多奇怪问题,狐表解决不了的,它补充。
所以就会想,如果我用python写好的功能,能被狐表调用,日志也融合进去狐表展示,无缝衔接,就太好了。
对,这个教程就是为了这个!
1基础教程
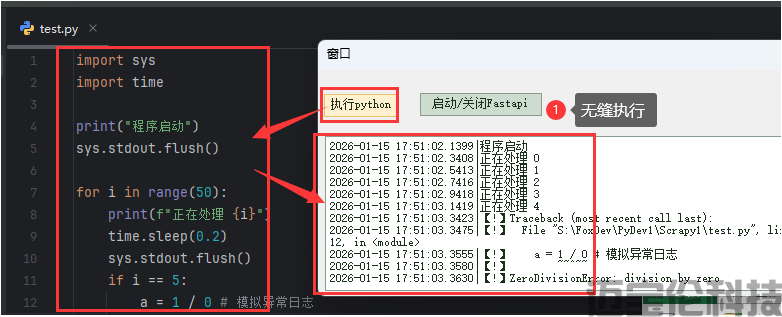
通过pycharm,已经把python代码都写好,调试好了,然后通过狐表触发cmd去执行python代码.
这种是最简单,不依赖于什么奇怪第三方库,这就是原生python会支持的一种方式。
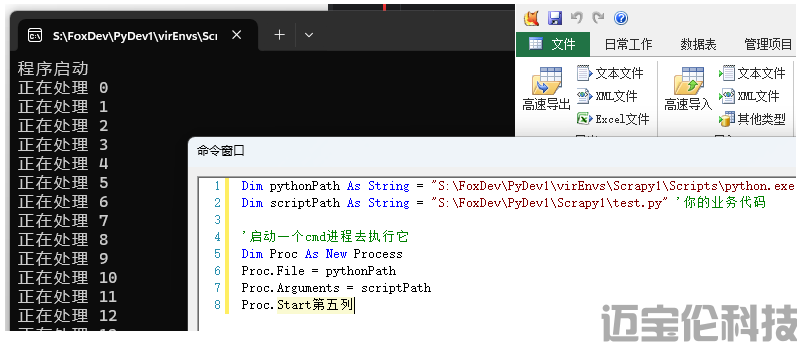
Dim pythonPath As String = "S:\FoxDev\PyDev1\virEnvs\Scrapy1\Scripts\python.exe" 'python环境地址 Dim scriptPath As String = "S:\FoxDev\PyDev1\Scrapy1\test.py" '你的业务代码 '启动一个cmd进程去执行它 Dim Proc As New Process Proc.File = pythonPath Proc.Arguments = scriptPath Proc.Start
2进阶优化
刚才狐表通过proc调用cmd触发python,虽然成功运行,但是日志内容,都飞出去了外置的cmd黑色弹窗框,不够优雅。
最理想是在Textbox直接看到python执行日志,让用户感知不到外部调用python

1)添加全局代码

命名:CmdLogCatch
Public Sub CmdOnOutput(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.Diagnostics.DataReceivedEventArgs)
If e.Data IsNot Nothing Then
Functions.Execute("CmdLog", "正常", e)
End If
End Sub
Public Sub CmdOnError(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.Diagnostics.DataReceivedEventArgs)
If e.Data IsNot Nothing Then
Functions.Execute("CmdLog", "异常", e)
End If
End Sub2)添加内部函数
函数名:CmdLog
代码:
'把Cmd获取到的日志,转移到TextBox展示
Dim log_type As String = Args(0)
Dim e As System.Diagnostics.DataReceivedEventArgs = Args(1)
If Forms("窗口1").Opened Then
Dim cb1 As WinForm.TextBox = Forms("窗口1").Controls("TextBox1")
'1底部追加新内容
cb1.Text &= Format(Now, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.ffff") & "|" & IIf(log_type = "正常", "", "【!】") & e.Data & vbCrLf
'2行数控制
Dim max_lines As Integer = 3000
Dim text_all_lines() As String = cb1.Text.Split(vbCrLf)
If text_all_lines.Length > max_lines Then
'只保留最新的N行
Dim s As String
For i As Integer = 1 To max_lines - 1
s &= text_all_lines(i) & vbCrLf
Next
cb1.Text = s
End If
'3自动滚动到底部(可选,如果希望始终显示最新内容)
cb1.SelectionStart = cb1.Text.Length ' 将光标定位到文本末尾
Dim d = cb1.BaseControl ' 获取底层基础控件
d.ScrollToCaret ' 滚动到光标位置,注意不能跟上一个连写,会报错
End If顺便准备一个窗口和Textbox1,去承载日志内容
3)执行按钮
Dim pythonPath As String = "S:\FoxDev\PyDev1\virEnvs\Scrapy1\Scripts\python.exe" 'python环境地址
Dim scriptPath As String = "S:\FoxDev\PyDev1\Scrapy1\test.py" '你的业务代码
Dim proc As New Process()
With proc.StartInfo
.FileName = pythonPath
.Arguments = scriptPath
.UseShellExecute = False
.CreateNoWindow = True
.RedirectStandardOutput = True
.RedirectStandardError = True
End With
AddHandler proc.OutputDataReceived, AddressOf CmdOnOutput '把常规日志关联到CmdOnOutput事件
AddHandler proc.ErrorDataReceived, AddressOf CmdOnError '把异常日志关联到CmdOnOutput事件
e.Form.Controls("TextBox1").Text = "" '清空日志
proc.Start() '开始执行
proc.BeginOutputReadLine()
proc.BeginErrorReadLine()4)Python代码的日志写法
日志需要sys.stdout.flush()才会立刻输出给控制台,否则会执行完所有,才一次过输出,在狐表Textbox就看不到逐行输出。
import sys
import time
print("程序启动")
sys.stdout.flush()
for i in range(50):
print(f"正在处理 {i}") # 演示常规日志效果
time.sleep(0.2)
sys.stdout.flush()
if i == 2:
a = 1 / 0 # 演示报错日志效果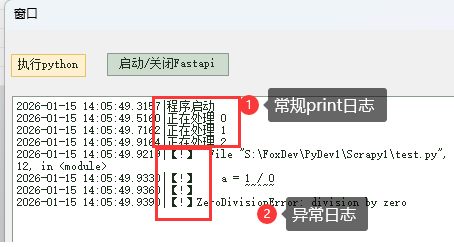
5)关于Fastapi这种启停类的
刚才的教程,都是执行一次。有时候,我们是需要启动蕾西Fastapi这种有状态,能控制启动和关闭的。
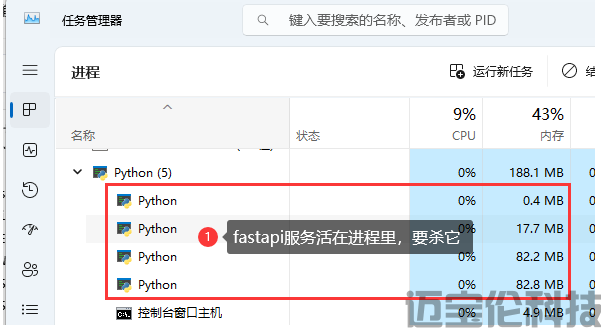
首先要清楚,Fastapi启动和关闭,它属于Window进程,跟狐表、cmd窗口打开或关闭无关。
所以要停止Fastapi服务,都是要杀进程的。
因此可以一个全局变量,启动后,存着这个proc,之后就用回它自杀即可
'启动Fastapi
Dim pythonPath As String = "S:\FoxDev\PyDev1\virEnvs\py311_fastapi1\Scripts\python.exe" 'python环境地址
Dim scriptPath As String = "-m uvicorn main:app --port 8001 --workers 2" '启动指令
Dim proc As New Process()
With proc.StartInfo
.FileName = pythonPath
.Arguments = scriptPath
.WorkingDirectory = "S:\FoxDev\PyDev1\web_project1\fastapi1" '设置Web程序运行目录
.UseShellExecute = False
.CreateNoWindow = True
.RedirectStandardOutput = True
.RedirectStandardError = True
End With
AddHandler proc.OutputDataReceived, AddressOf CmdOnOutput
AddHandler proc.ErrorDataReceived, AddressOf CmdOnError
e.Form.Controls("TextBox1").Text = "" '清空日志
proc.Start() '开始执行
proc.BeginOutputReadLine()
proc.BeginErrorReadLine()
'2杀死Fastapi进程。这里演示,就把代码连着放。合理把刚才的proc应该存全局变量,然后这里拿出来自杀
MessageBox.Show("卡主,确定后就会停止Fastapi")
If proc IsNot Nothing AndAlso Not proc.HasExited Then
proc.Kill()
End If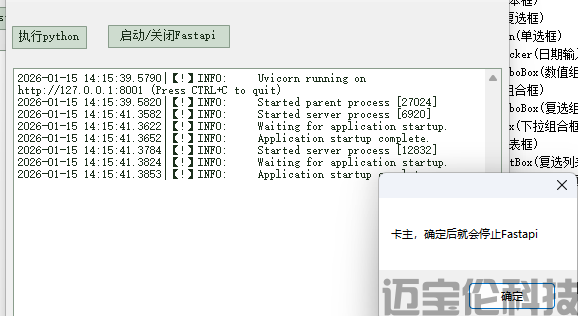
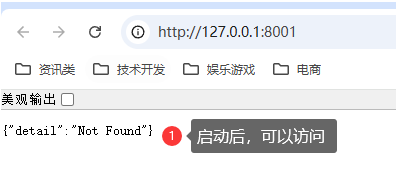
3如何更新python给客户
由于python作为外挂,自身库有一定大小,又经常下载各种新库,所以不适合连着狐表项目一起打包
更加推荐,把python项目,整个放到某个网站。等客户要执行的时候,才去联网检查新版本,下载最新文件。
随便看看